Welcome to the lava.top API portal!
Introduction
If anything is unclear, feel free to contact our support team: support@lava.top.
General Information
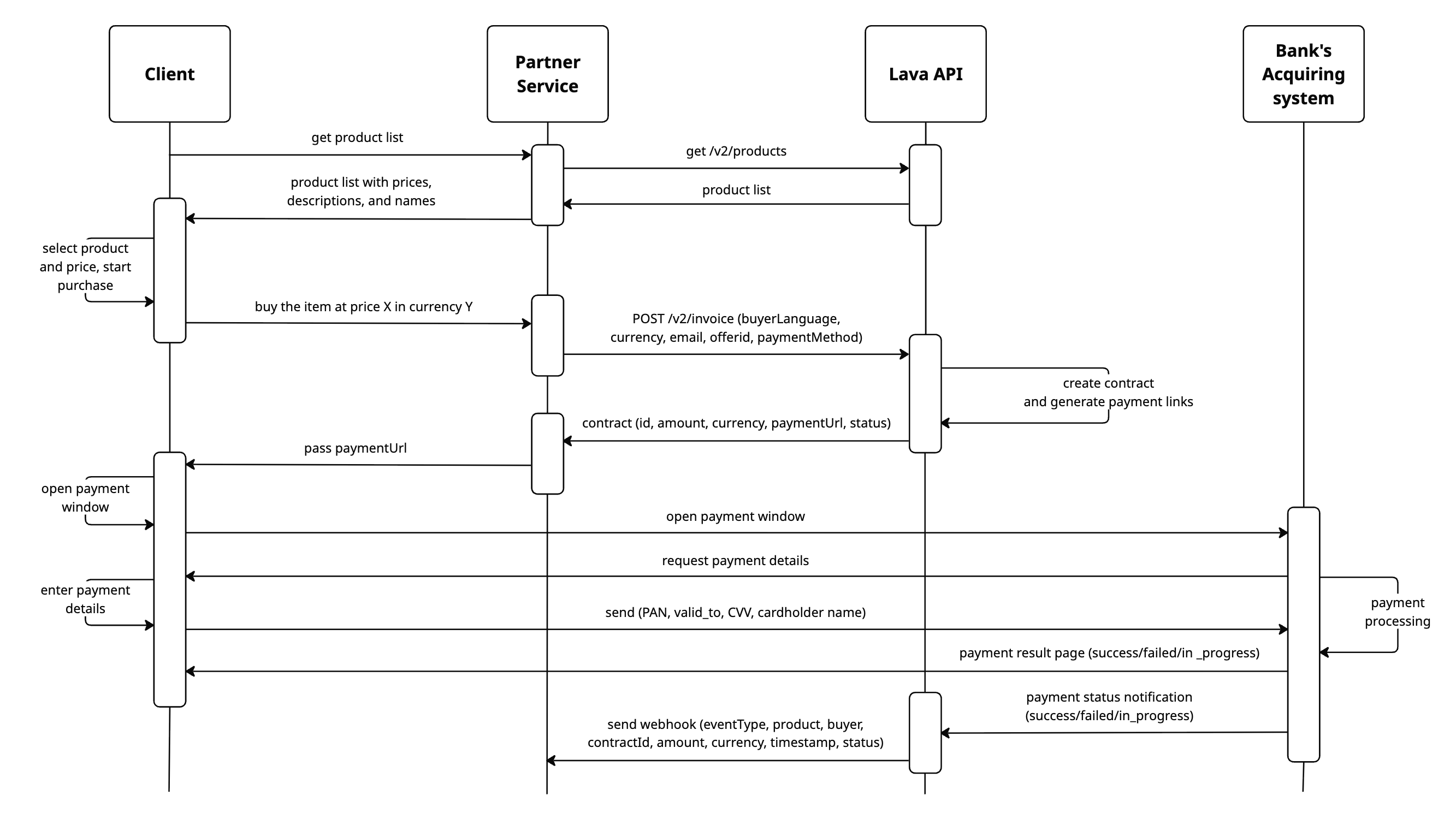
Integration is the process of connecting two or more services using an API. It allows systems to exchange data and events, enabling them to work together in an automated and coordinated way.
With lava.top, you can set up integration with any external system, service, website, or Telegram bot — to accept and track payments, manage access, and control subscription statuses. This makes your workflows simpler and more convenient.
Public API — lava.top's public programming interface that allows external software and applications to interact with each other over the network.
API Key — a unique code used for the authorization and authentication of an API client. Think of it as a login and password, but for software — without it, you can't access the data or features provided by the API.
Webhook — a mechanism that allows one service to automatically send data to another in response to certain events. In simple terms, it’s a notification your system receives when something happens. Instead of constantly asking the server “what’s new?”, you configure a URL once, and the server notifies you when needed.
Typical scenarios for using our API:


API Key and Webhook Setup
To get started with integrating your service on the platform, you need to create an API key and set up a webhook.
How to Create an API Key
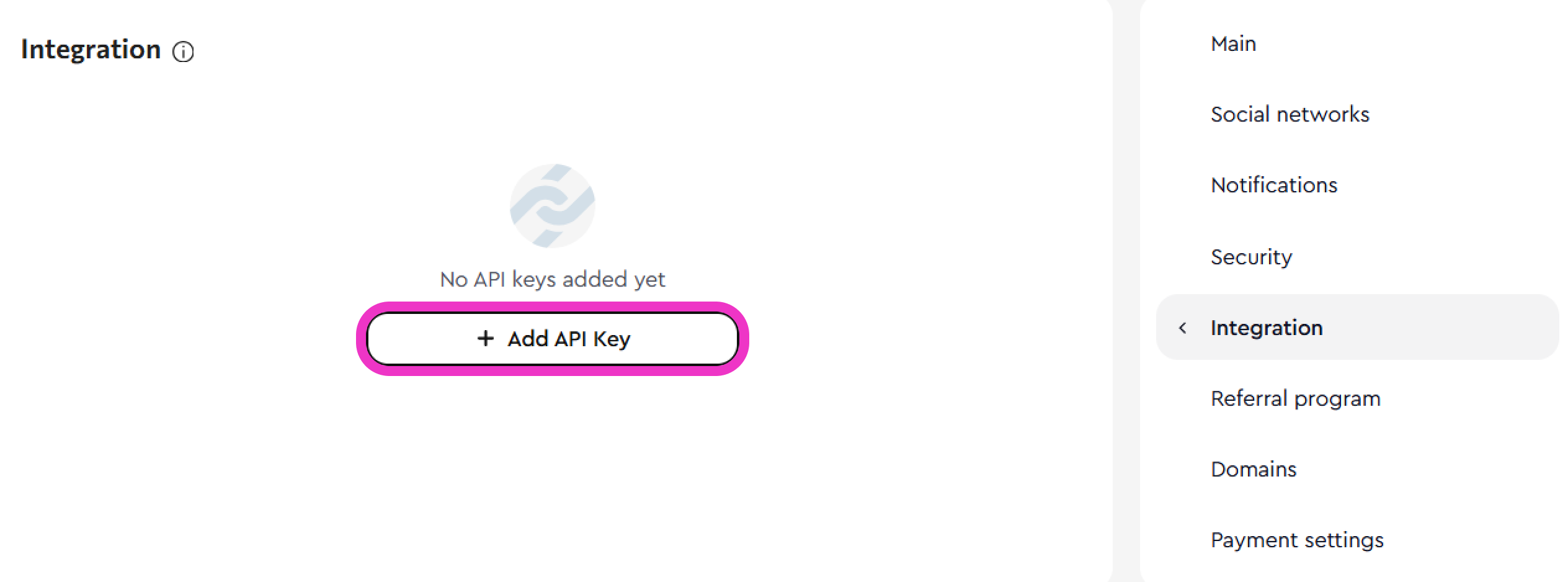
- Go to the My Page section and click Profile in the top-right corner.
- Navigate to the Integration tab and click Add API Key.

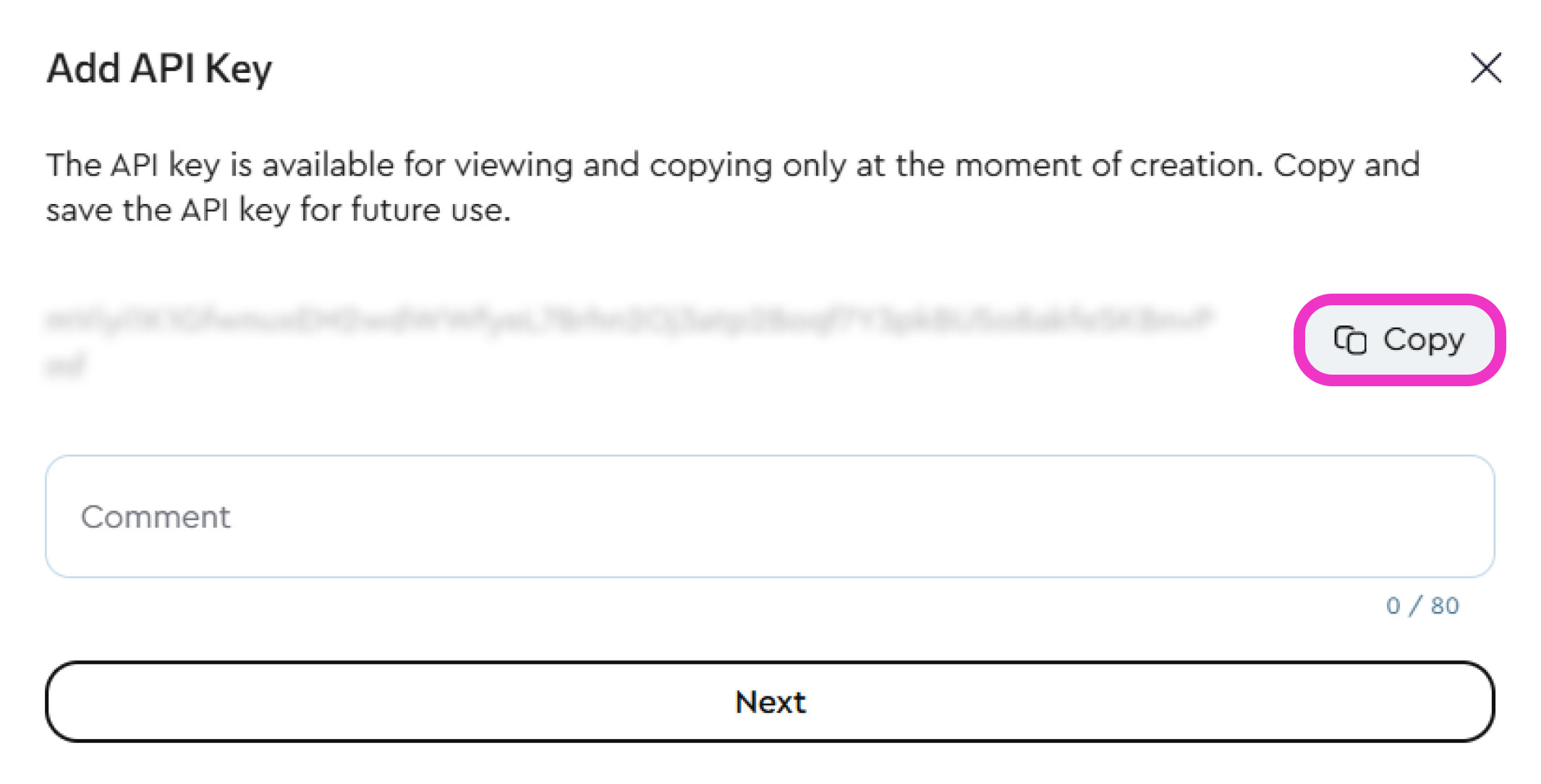
- The platform will generate the key automatically — copy it and save it securely on your device.

How to Set Up a Webhook
- Create an API key and confirm that you’ve saved it.
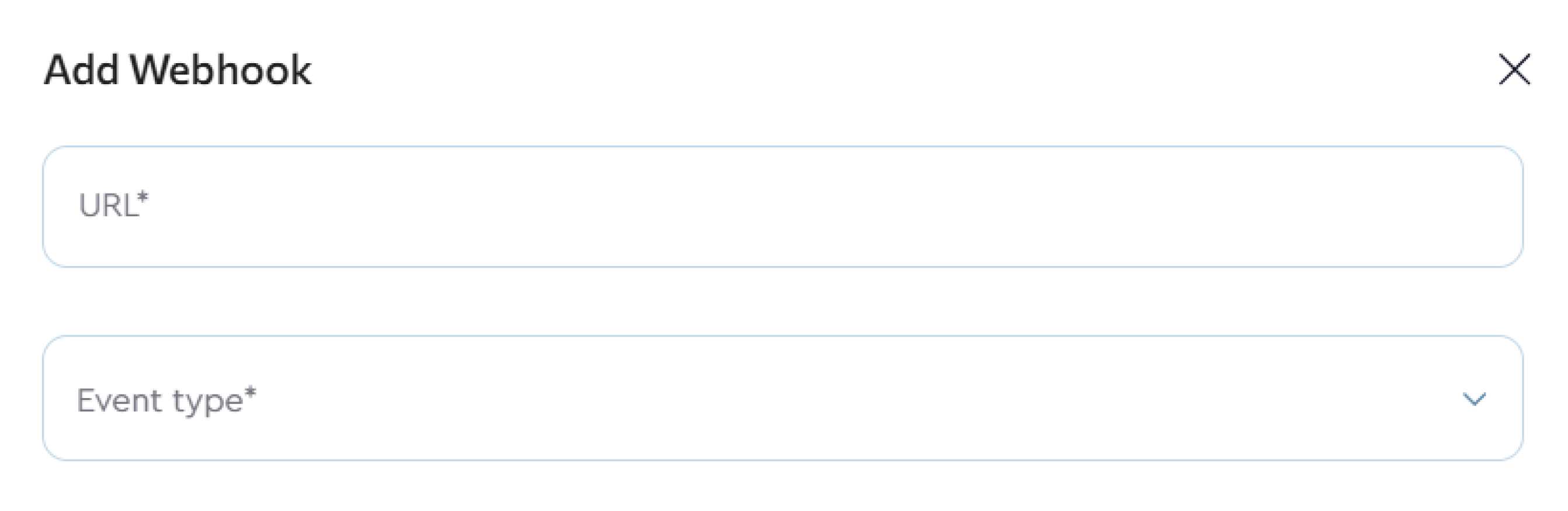
- Click the Add Webhook button.


- Fill in the following fields:
- URL — the endpoint on your server where webhook data will be sent (this is the address that will receive and process requests).
- Event type:
- Payment result — one-time purchase: use this type for one-time payments as well as the first payment in a subscription.
- Recurrent payment — subscription payment: used for second, third, and all subsequent subscription charges.

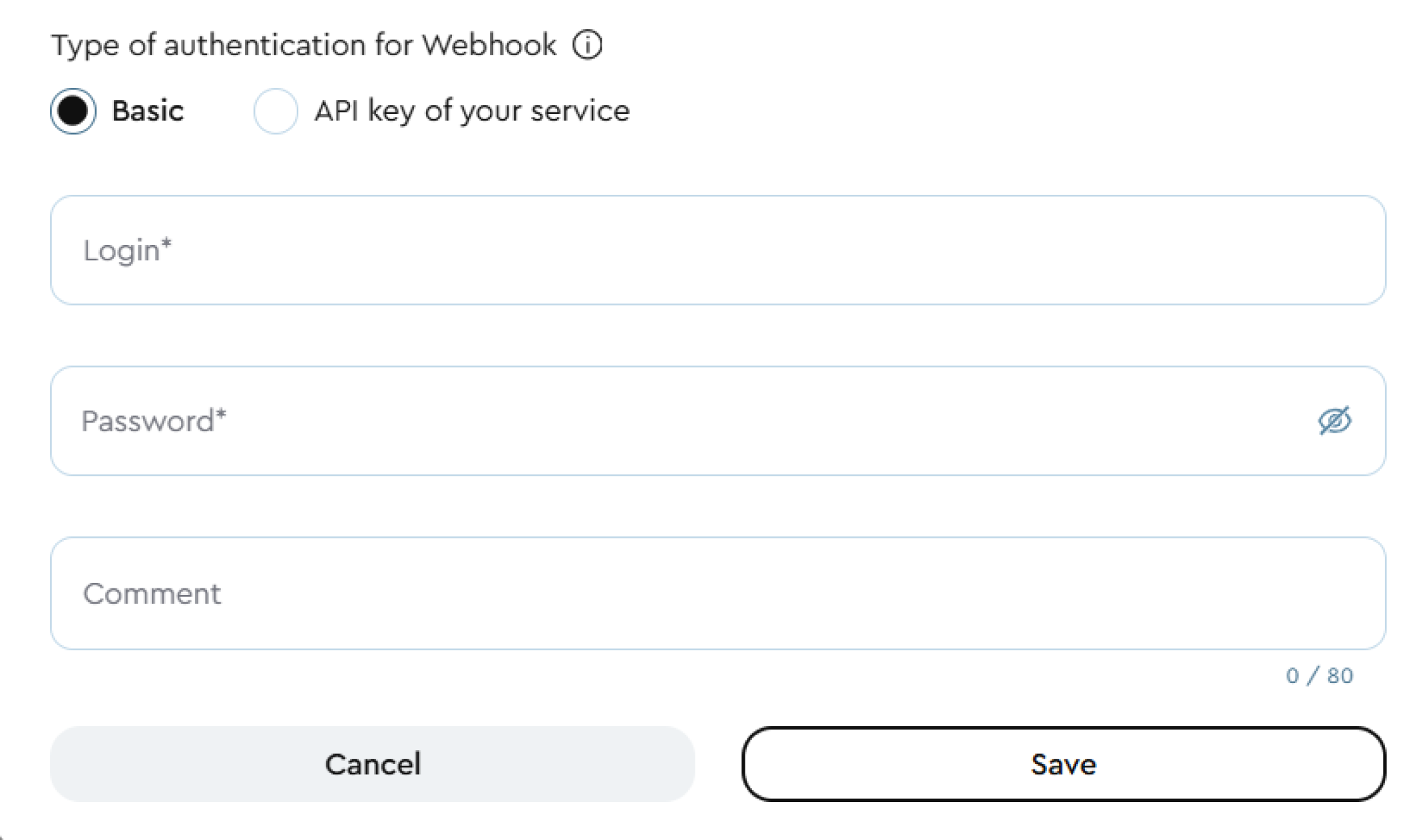
- Choose an authentication method:
- Basic - enter the login and password for your service that will receive webhook requests.

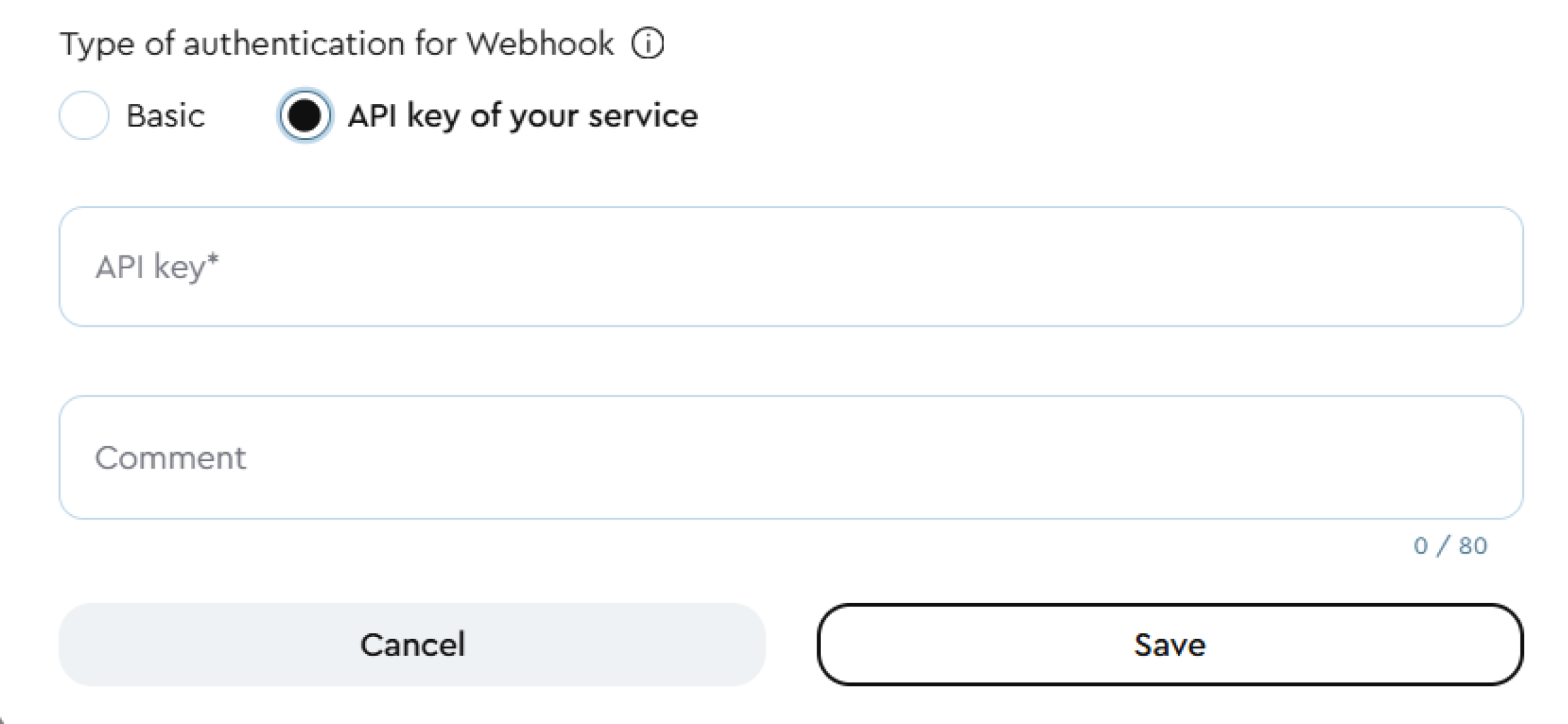
- Your service’s API key - enter the API key of your service that will receive the webhook requests. Maximum key length: 80 characters.

Basic authentication: lava.top will send webhook requests to the specified URL using HTTP Basic Authentication. The request will be sent in the format: user:pass@example.com. Only HTTPS connections are allowed for this type of request to ensure security.
API Key Authentication: lava.top will send webhook requests to the specified URL, authenticated using an API key.The receiving server must extract the key from the HTTP header: "X-Api-Key".
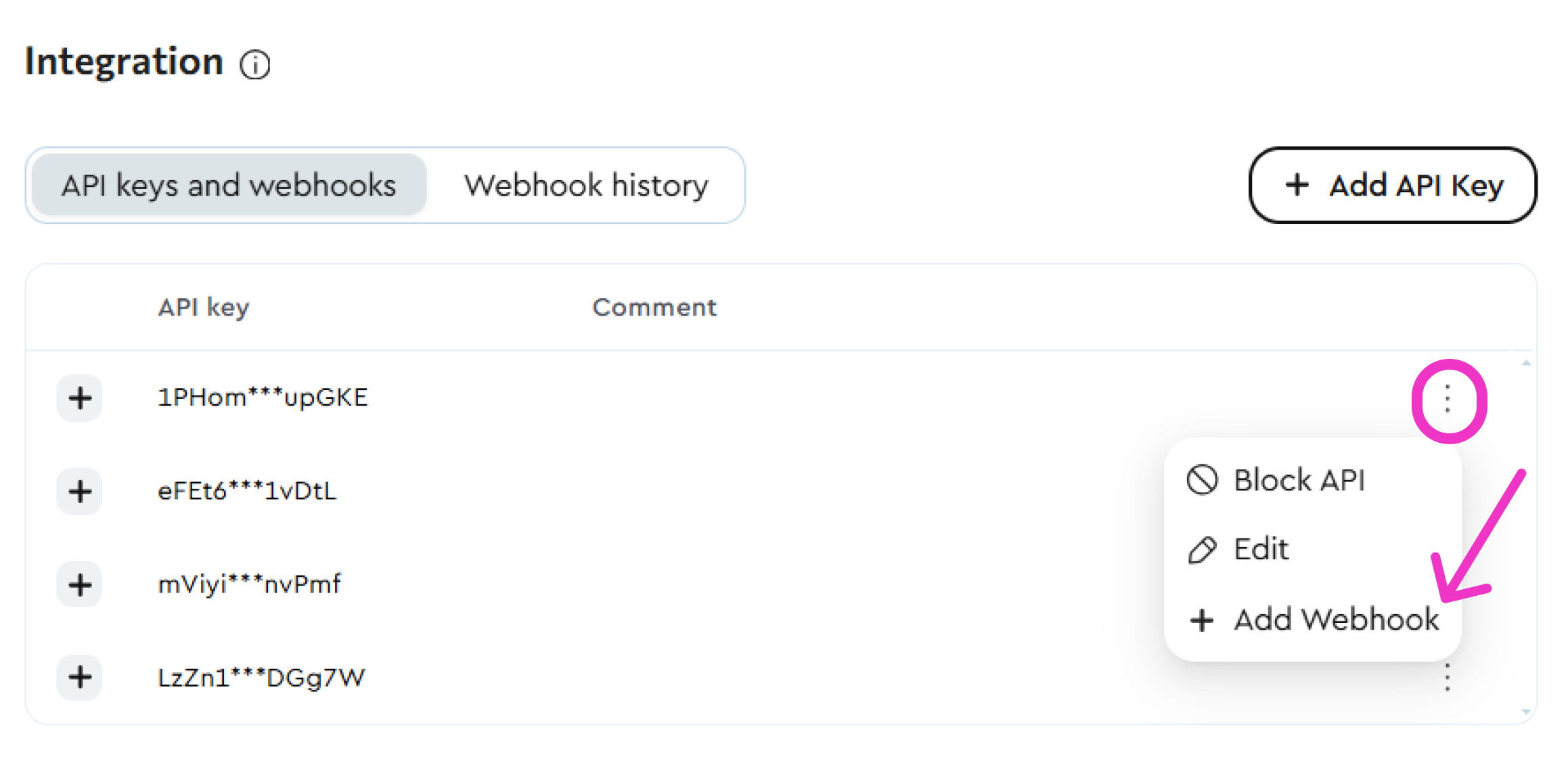
Click the three dots next to the desired key and select Add Webhook.

API Documentation
API Documentation
To get a detailed overview of available API methods, refer to our API documentation.
The documentation follows the Open API v3.0.0 (Swagger) specification.
You can find API methods grouped by the most common use cases:
Products - work with digital products: fetch the product list and update their parameters (e.g., price).
Invoices - create purchase contracts and check their status.
Reports - access sales analytics data via the API.
Subscriptions - manage user subscriptions.
Donate - generate donation links.
Interactive documentation allows you to test each method and ensure it works correctly.
- provide your API key:
- Click Authorize in the top-right corner of the page:
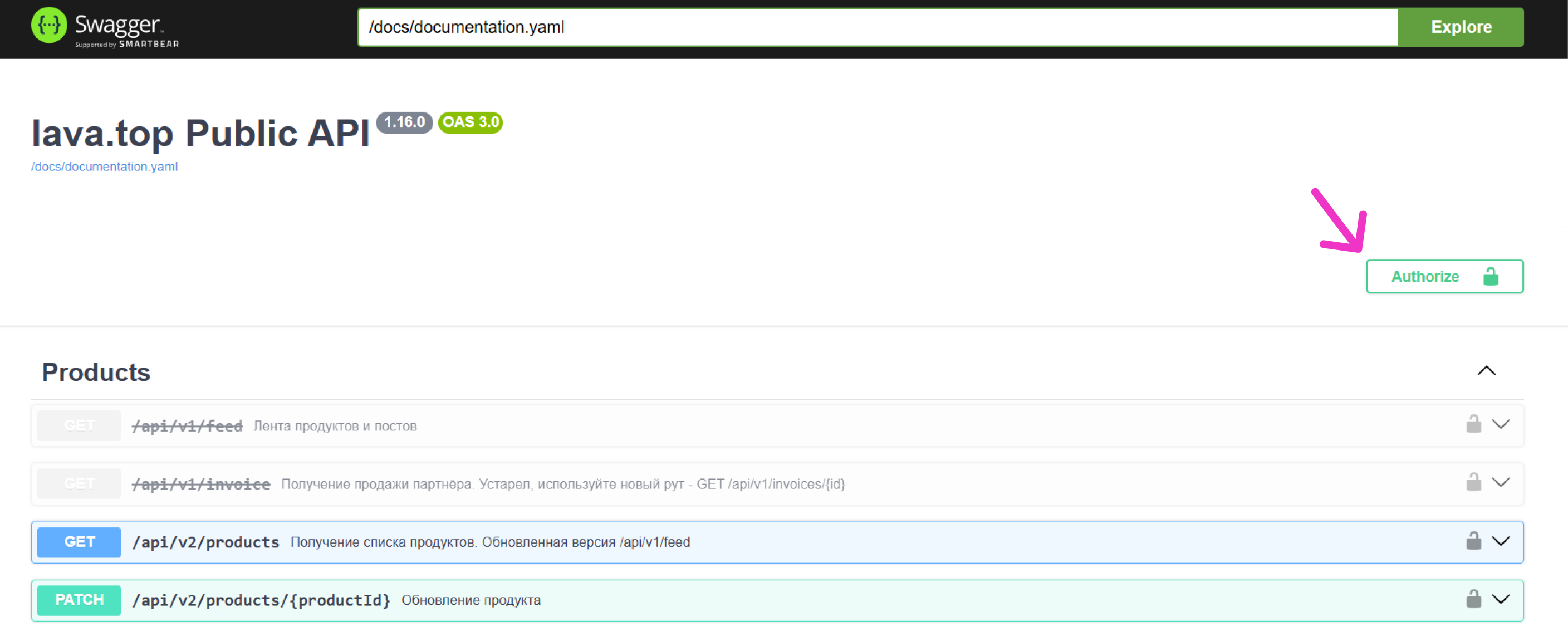

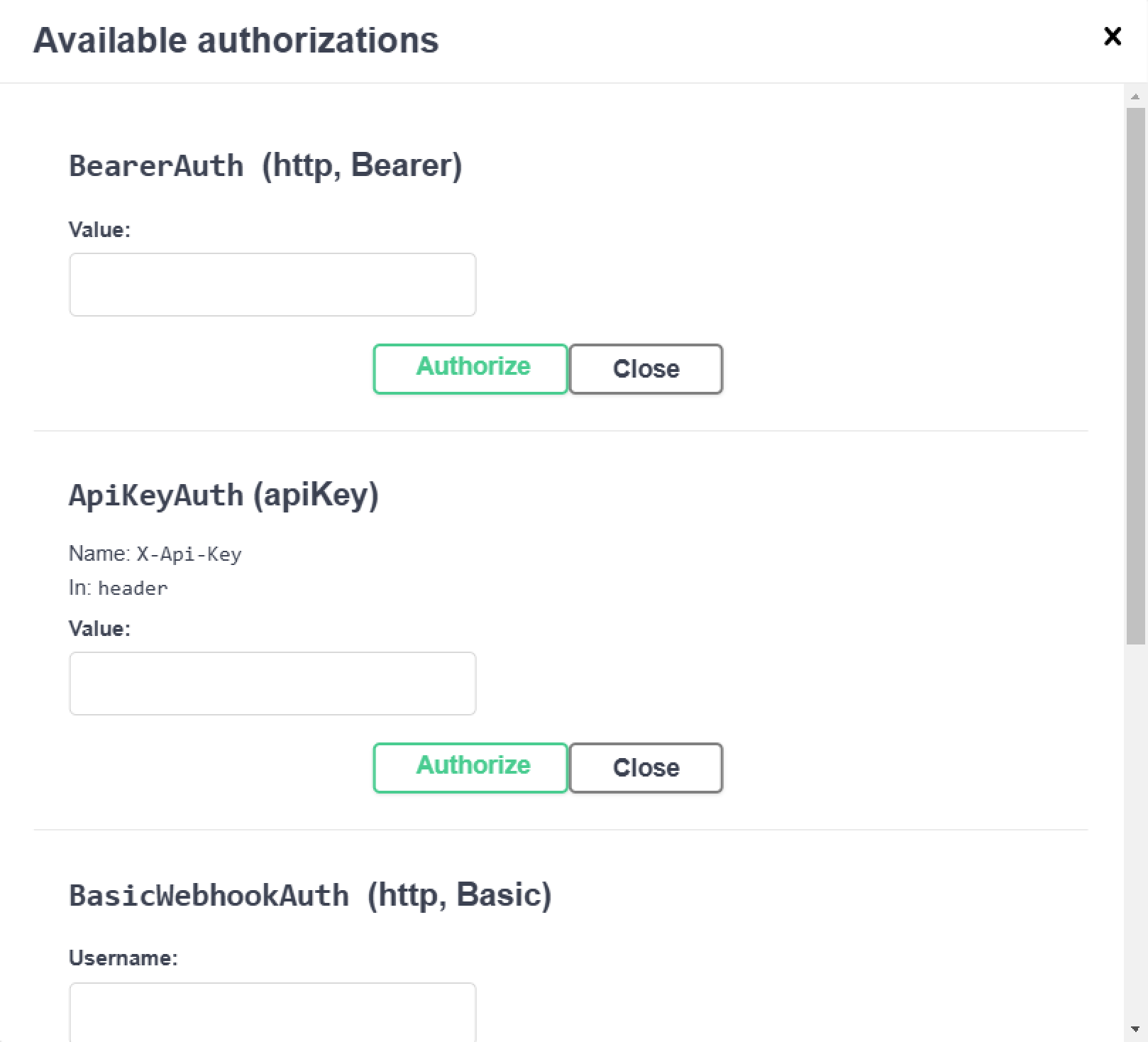
- fill in ApiKeyAuth (apiKey), (use the API key you received in the Author’s personal account interface at lava.top: My Page → Profile → Integration → Add API Key (we explained this in more detail here)):

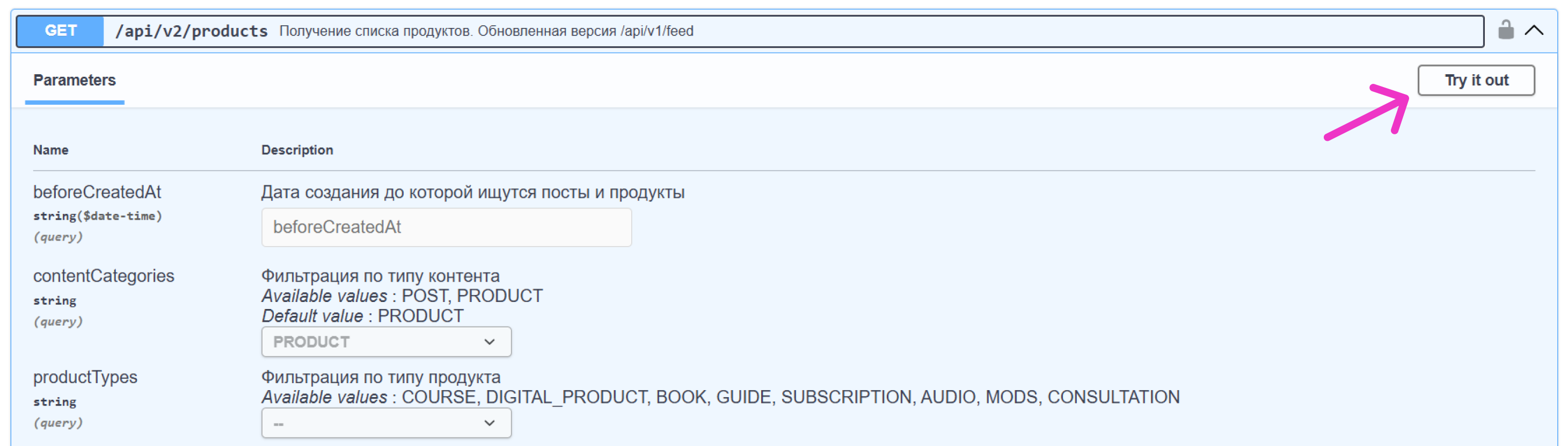
- click Try it out, enter the required data, and select Execute:

API Libraries
API Libraries
We’ve prepared several open-source libraries to help you use our platform more easily and efficiently.
Our API follows the Open API (Swagger) specification, which can be complex to work with — these libraries are designed to simplify the process.
!Python
Get the package PyPI, typically via pip:
1.pip install lava-top-sdk
Make sure that, however you install lava-top-sdk, you install its dependencies as well.
!TypeScript
Available on npm
1.npm install --save lava-top-sdk
Clients and API Keys
Clients and API Keys
Lava.top uses two types of API keys, each serving a specific role in the integration process:
This key is used by your system to send API requests to lava.top. It allows us to identify and authorize your application.
This key is generated on your side and shared with lava.top. The platform uses it to sign webhook requests by adding it to the X-Api-Key HTTP header when sending data to your server.
Errors
Errors
Lava.top uses standard HTTP response codes to indicate whether an API request was successful or if an error occurred.
All outgoing connections originate from the IP address 158.160.60.174
If the webhook is not delivered, the system will automatically try to resend it to the specified URL. The first attempt will be in one second, the second in five seconds, and the third in 15 seconds. The system will then make ten attempts with an interval of one minute. After that, if unsuccessful, the system will make five more attempts with an interval of one hour.
Up to 20 attempts will be made in total.
The most common errors:
| Code | Descriprion |
|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request: The request is invalid. Check syntax, parameters, size limits, etc. |
| 401 | Unauthorized: Authentication error. Verify your API key, OAuth token, token expiration, or required scopes. |
| 403 | Forbidden: Access to the resource is denied. You may lack permissions or be trying to access a restricted resource. |
| 404 | Not Found: The resource was not found. Check the URL, object ID, or whether the resource exists in your account. |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed: The HTTP method is not supported for this endpoint. Refer to the API documentation. |
| 406 | Not Acceptable: Unsupported request or response format. The API only supports application/json. |
| 408 | Request Timeout: The server timed out waiting for the request to complete. Try resending with smaller data payloads. |
| 410 | Gone: The resource has been permanently deleted and is no longer available. |
| 429 | Too Many Requests: Rate limit exceeded. Reduce the frequency of requests. |
| 500 | Internal Server Error: A server-side error occurred. Try again later. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable: The service is temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or overload. Please try again later. |
Rate Limits
Rate Limits
Lava.top applies request rate limiting to protect against overload and ensure stable API performance.
Webhook
Webhook
As mentioned earlier, in the Integration section of the Author’s profile settings, you can create API keys and add webhooks.
You can also view the sending attempt history, check the status of each webhook, and re-send any webhook that failed to be delivered or processed.
!Webhook History
You can find the webhook history in your account card. To access it, go to Profile Settings → Integration → Webhook History.
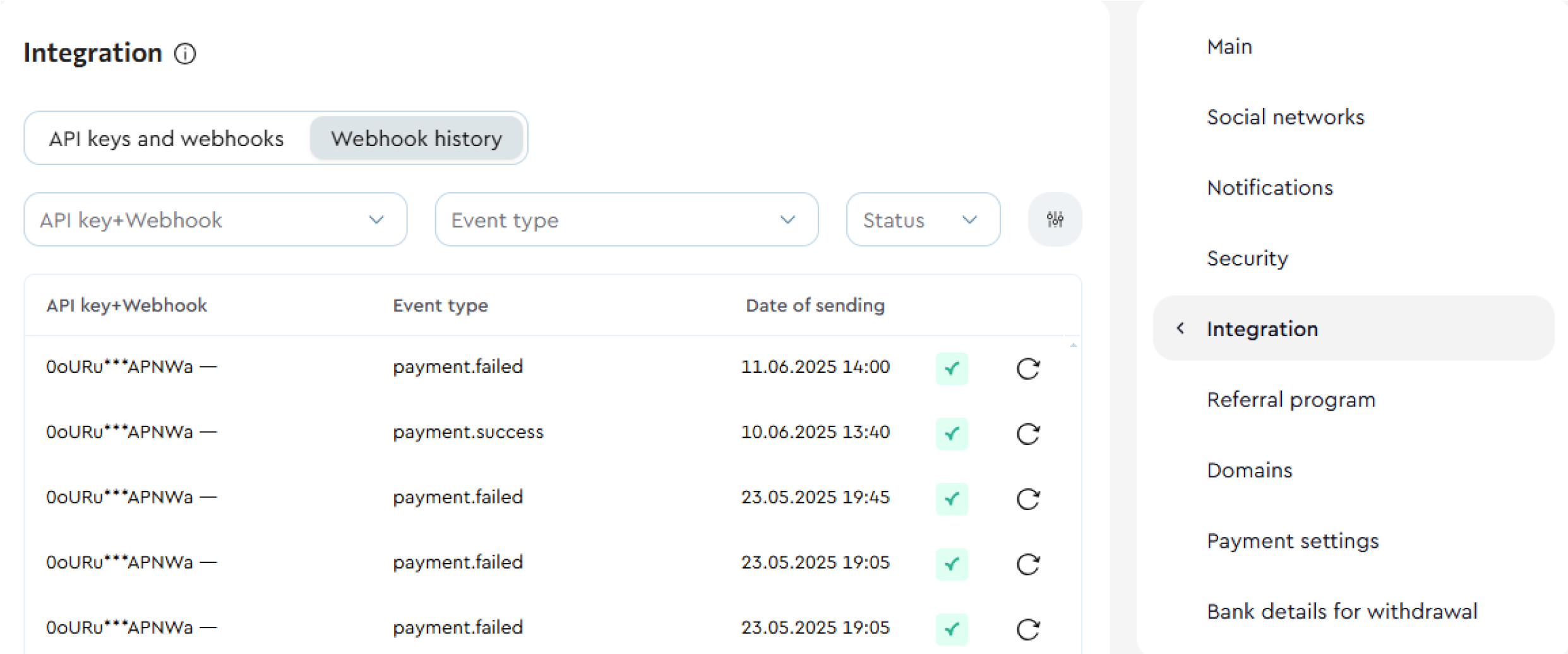

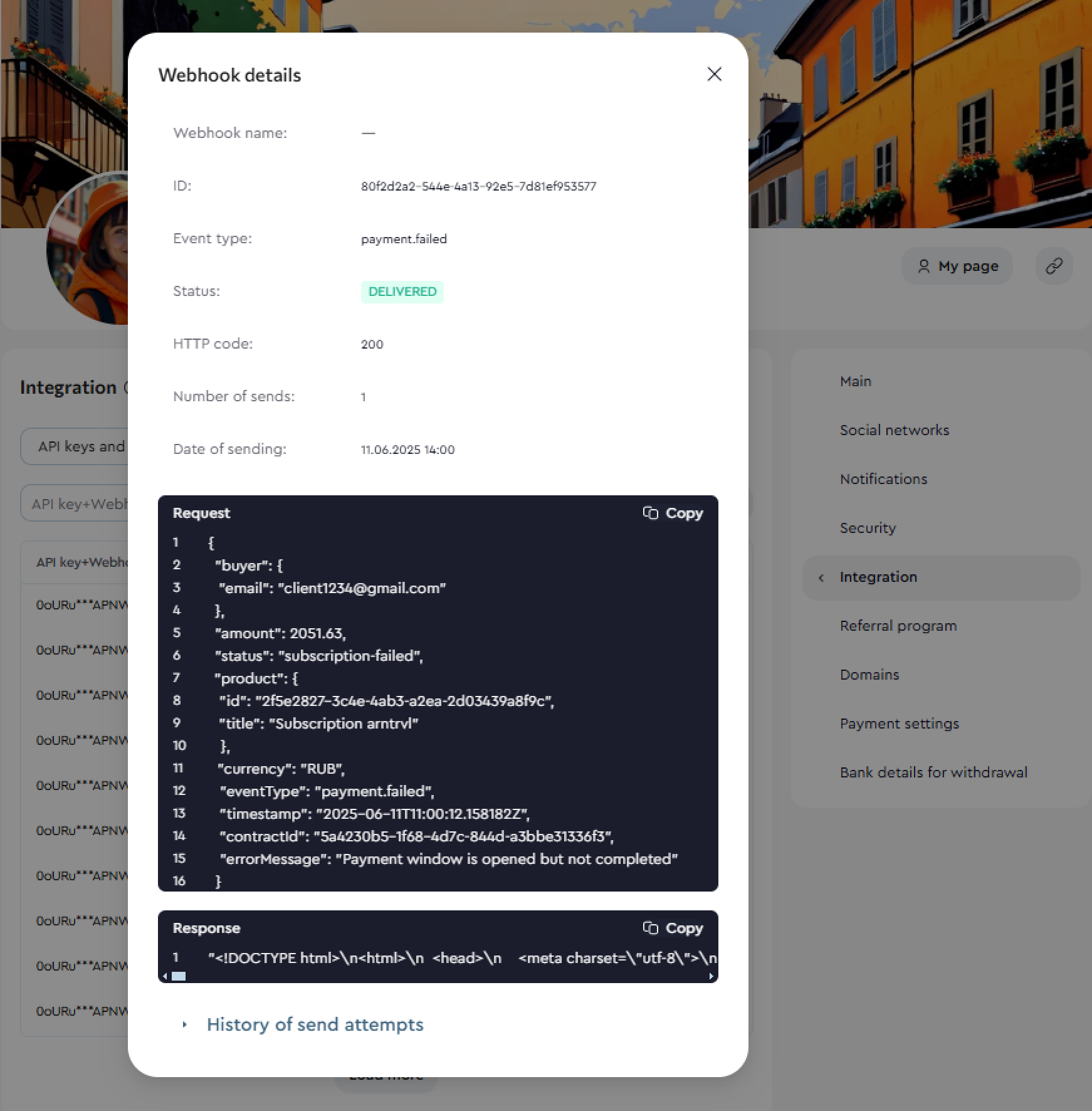
This section logs all events linked to your configured webhooks. Events are categorized by type, status, and the API Key + webhook pair.
In the payment details, you can view the full request body sent at the time of the event, along with the delivery attempt history. To see these details, simply click on the corresponding webhook entry.
Advanced filters are available to help you quickly find the webhook you need — you can search by Buyer's email, Invoice ID, Product name, or Product ID.

!Events Types
Each event is associated with a payment type and a contract status.
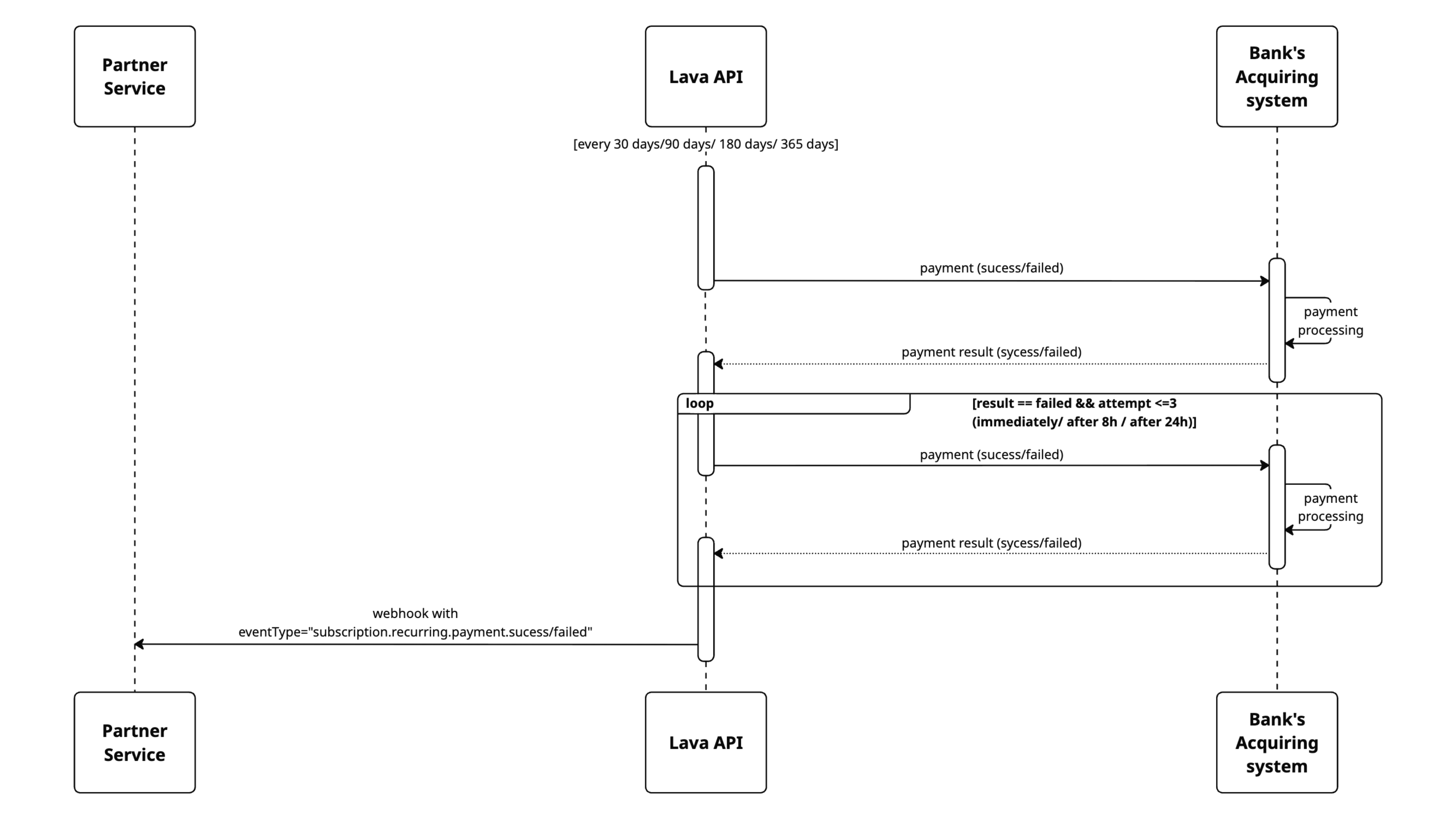
Payment Types:
- one-time payment (purchasing a digital product, course, consultation, or the first payment in a subscription);
- recurring payment (subscription renewal or cancellation).
Contract Statuses:
- success (payment was successful);
- failed (payment was not completed, e.g. insufficient funds);
- cancelled (the subscription was cancelled).
Based on this, you may encounter the following Event types:
- payment.successpayment.success — successful purchase of a product (not a donation) or the first subscription payment;
- payment.failedpayment.failed — failed product purchase (not a donation) or failed first subscription payment;
- subscription.recurring.payment.successsubscription.recurring.payment.success — successful renewal of a subscription (second, third, and later payments);
- subscription.recurring.payment.failedsubscription.recurring.payment.failed — failed subscription renewal;
- subscription.cancelledsubscription.cancelled — cancellation of a previously active subscription.
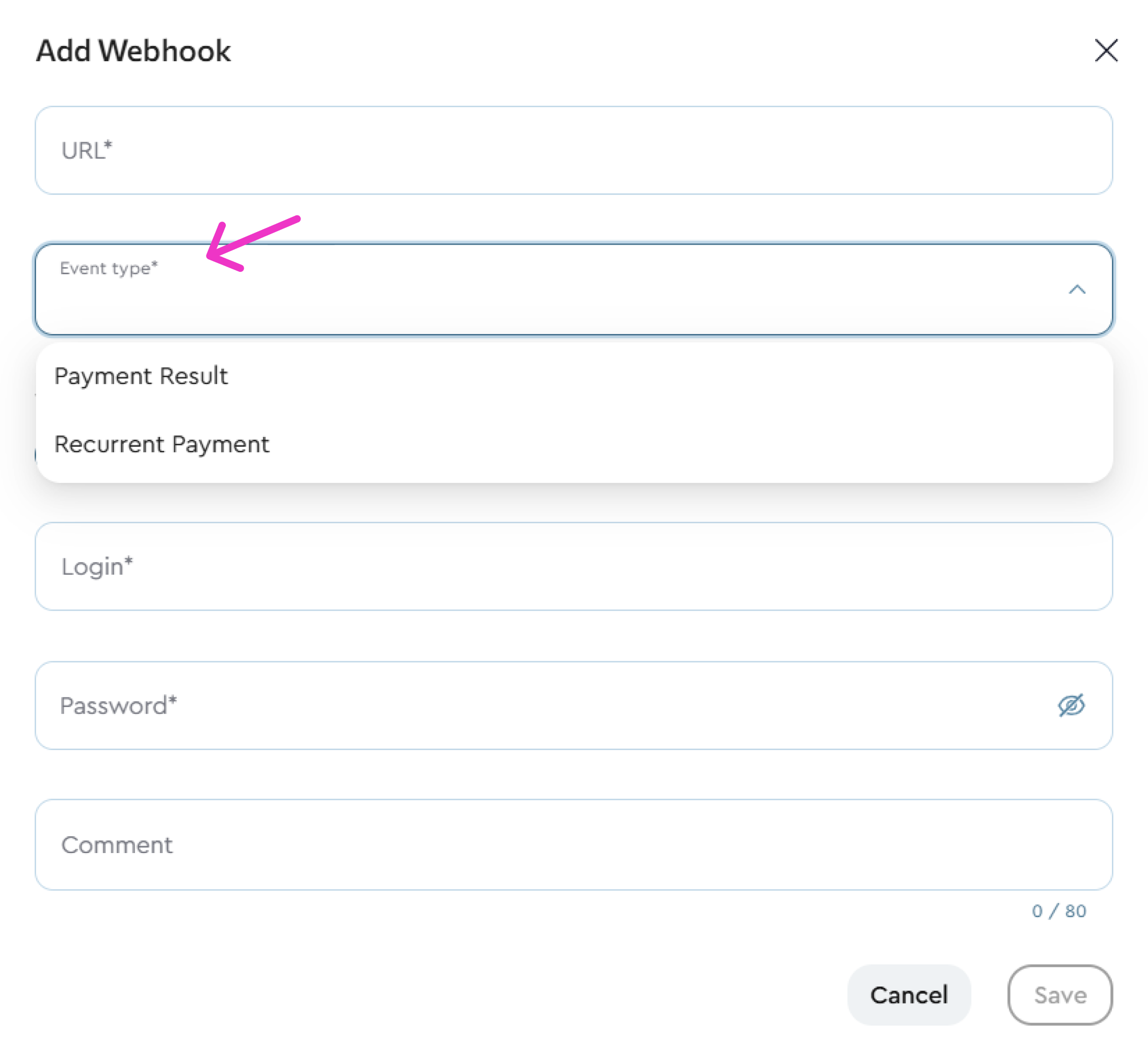
To receive these events, you need to set up the appropriate webhook. When creating a webhook, you must choose one of the two event types:
- Webhook with type Payment result (receives only payment.successpayment.success and payment.failedpayment.failed .)
- Webhook with type Recurring payment (receives only subscription.recurring.payment.successsubscription.recurring.payment.success , subscription.recurring.payment.failedsubscription.recurring.payment.failed and subscription.cancelledsubscription.cancelled ).

!Webhook Status
The status indicates whether the webhook was successfully received.


A webhook can have one of two statuses:
- DELIVERED — the webhook was successfully delivered.
- FAILED — the webhook delivery failed.
The status is determined based on the HTTP response code returned by your server when the event is sent.
!Retry Policy
Lava.top uses HTTP status codes to determine whether an API request was successfully processed or failed.
If a webhook delivery fails (i.e., a non-successful HTTP status code is returned), lava.top will retry the delivery up to 19 additional times, for a total of 20 attempts.
If webhooks were not delivered, the system will attempt to resend them to the specified URL. Repeated attempts are made according to the logic: first 1s, 5s, 15s, then 10 attempts with an interval of 1 min, then, if unsuccessful, another 5 attempts with an interval of 1 hour.
In total, 20 delivery attempts will be made.
Each attempt is logged in the webhook history with the corresponding HTTP status code. If a successful status code is received, no further retries will be made. In that case, you’ll see only one event logged (successful or failed payment).
In case of an unsuccessful response, up to 20 attempts may be made (retries stop after a successful delivery or after 19 retry attempts).
You can view all retry attempts in the "Sending attempt history" section of the webhook details.
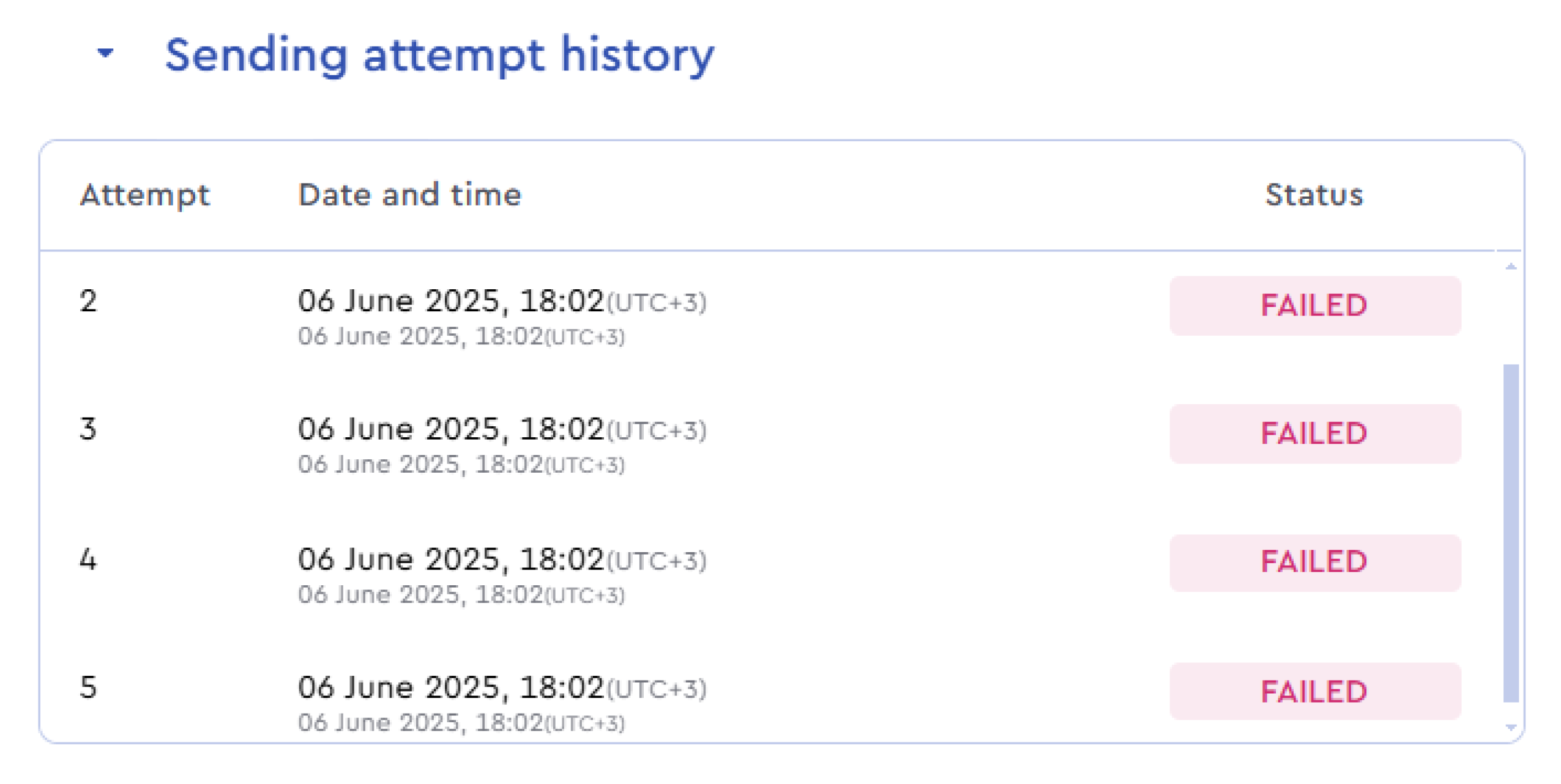

Most common response codes:
- Code 401 / Code 403 — Invalid authentication data; access to the webhook handler is denied;
- Code 404 — The webhook contains an incorrect URL (the link to the author's server that receives and processes the webhook is invalid)
- Code 500 — An error occurred on the author's server that is responsible for handling the webhook.


!Webhook Resend
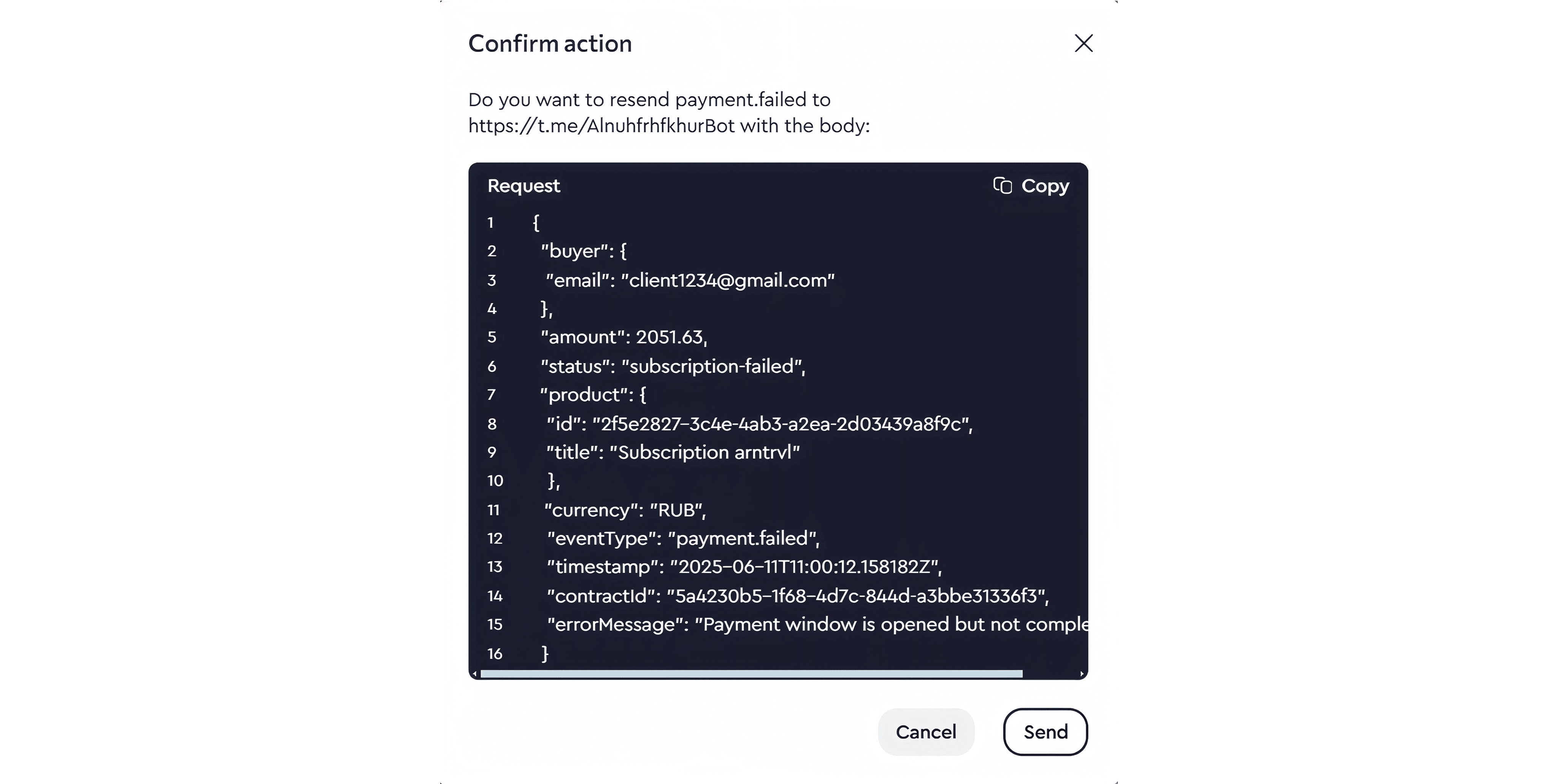
You can manually resend any webhook by clicking the arrow icon next to it.
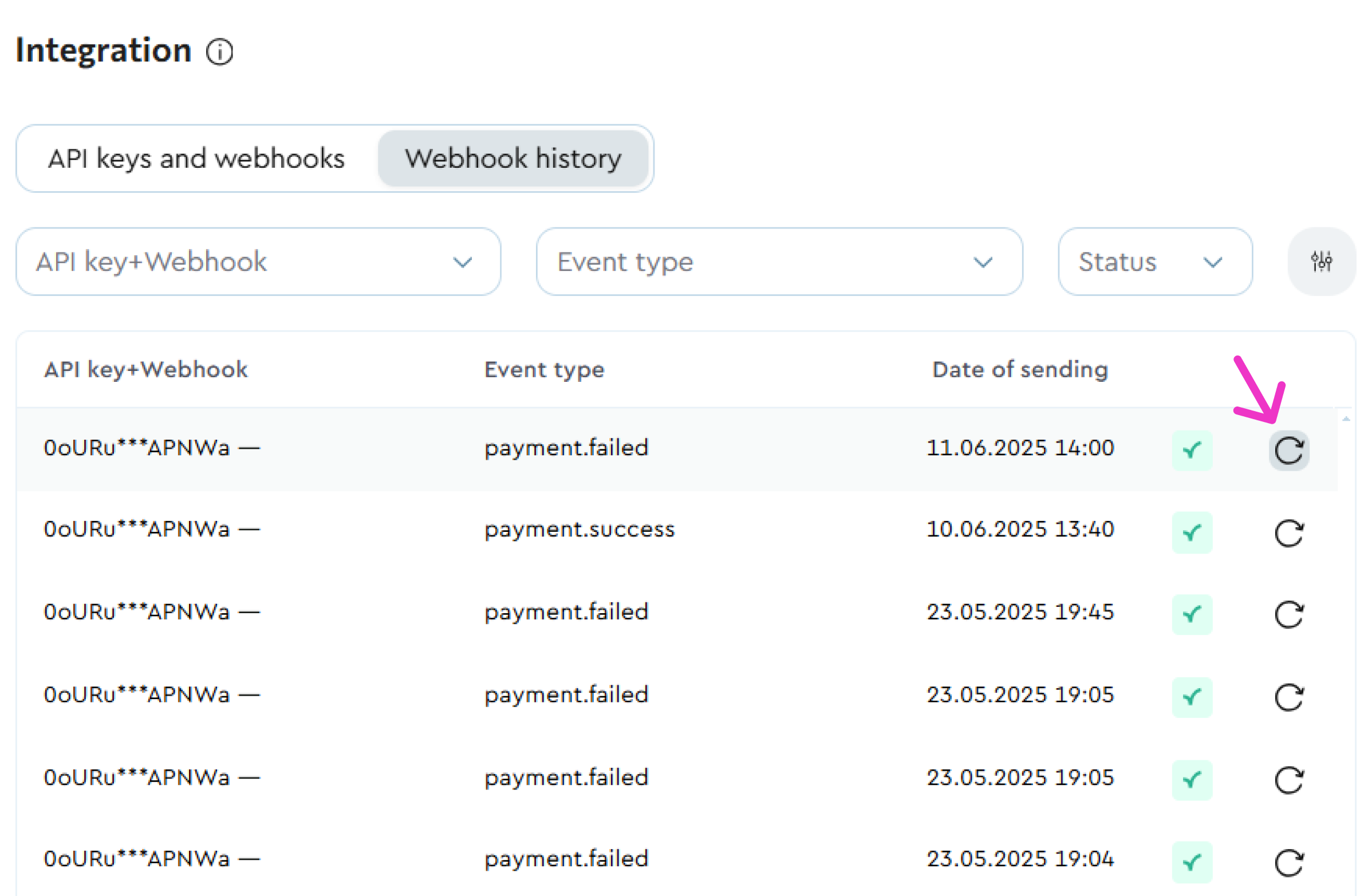

Click the icon and confirm the resend action.

Changelog
Changelog
We regularly improve integration capabilities by adding new features, fixing bugs, and updating the documentation. Here you can keep track of all the changes.
Subscription payments via Stripe are now supported.
Implemented /api/v2/invoices and /api/v2/invoices/{id} endpoints with updated contract typing:
- INVOICEINVOICE - payment for products, consultations, or courses,
- SUBSCRIPTION_FIRST_INVOICESUBSCRIPTION_FIRST_INVOICE - first subscription charge,
- SUBSCRIPTION_RENEWALSUBSCRIPTION_RENEWAL - recurring subscription payment.
Donation payments via Stripe are now supported.
Improved GET /invoices request: now returns the parentInvoiceId field (ID of the parent transaction for subscriptions).
PayPal support added:
- Subscription payments,
- Donation sending.
Webhook improvements:
- Manual retry option,
- Webhook list retrieval,
- Event type now included in the webhook payload,
- Ability to search webhooks by Product ID in the Author Dashboard (Profile → Integrations → Webhook History).
UTM tags added.
Stripe payment support added for digital products.
FAQs
FAQs
Here we've collected the most frequently asked questions that may come up when using our API.